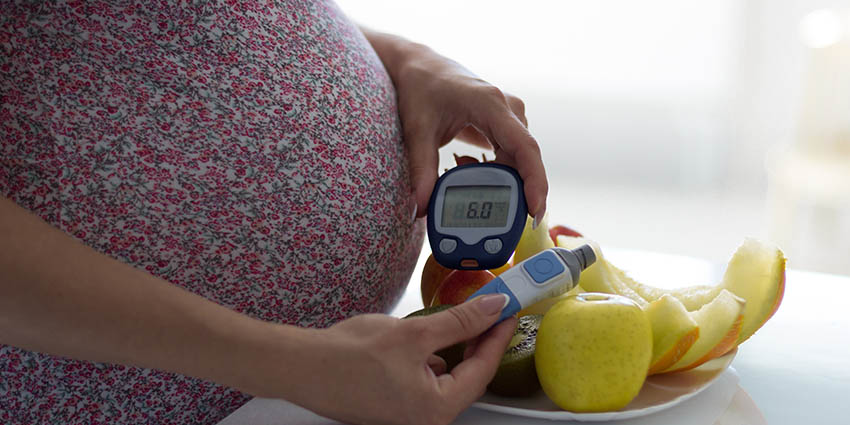
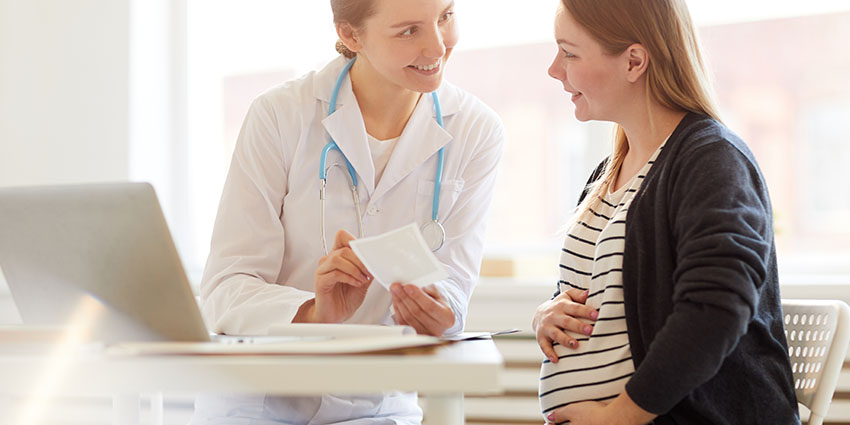
Gestational diabetes (GDM) is a term used to define abnormal blood sugar values that show up for the first time during pregnancy. It is different from women who have other types of this disease like Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. These other forms of diabetes are complications of pregnancy that are discussed in another article.
The hormones of pregnancy change the way that insulin is used by the body and therefore may increase the chance of developing GDM during any pregnancy. As the placenta grows larger during the pregnancy, that chance increases. There are also certain risks for GDM that your provider will discuss with you. They are things like obesity, hypertension, becoming pregnant over 35 years of age, a history of polycystic ovarian disease (PCOS), or a family history of diabetes.
Based on your medical and family history, you may be asked to obtain an early glucose (sugar) screen in your first or second trimester. Current recommendations are that all pregnant women receive testing at 24-28 weeks along in the pregnancy. This is usually a two-step process in which you will receive a sugary drink and then have a blood sugar test one hour after completing the drink. If this test is high, you will be ask to take a similar test lasting 3 hours to confirm a diagnosis of GDM.
Knowing if a woman has GDM is very important so that complications of pregnancy can be avoided if possible. A more complete description of complications and treatment of GDM are discussed in another article. Management of this pregnancy complication relies heavily on diet, exercise, and in some cases medication.
Related Posts